| |
|
|
| |
|
| |
 Research Highlights => Study of High Entropy Alloy Research Highlights => Study of High Entropy Alloy |
【Print】 【Back】 |
|
|
Published date: [8/26/2025]
Read [1262] times |
|
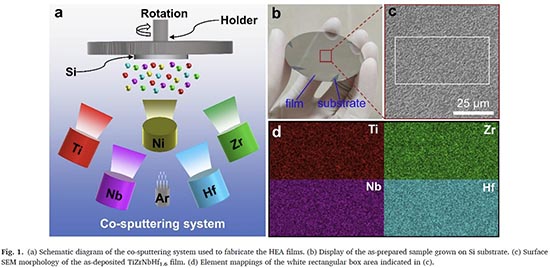
The research team in Central South University, China leaded by Prof. Jianjun Li had used Ti, Zr, Nb, Hf and Ni elemental targets to perform co-sputtering process to synthesize TiZrNbHf1.6Nix high entropy alloy HEA film. The microstructural analysis indicates that the TiZrNbHf1.6 film has a single body centered cubic BCC with columnar-nanograined structure. As Ni content increases to 0.4 or above, the films show a complete amorphous structure. It has shown that there are about 35% hardness increment in the Ni-doped alloy films. The elevated hardness may be attributed to the severe lattice distortion and the amorphous structure induced by the Ni addition. Their research works demonstrate that ultrastrong and highly deformable amorphous high entropy alloy thin films can be developed by appropriate element addition, making them promising materials for corrosion and wear-resistant coatings.
The research work is published in "Nickel content-dependent microstructure and mechanical properties of TiZrNbHfNi high entropy alloy thin films" .
========================================================
 ========================================================
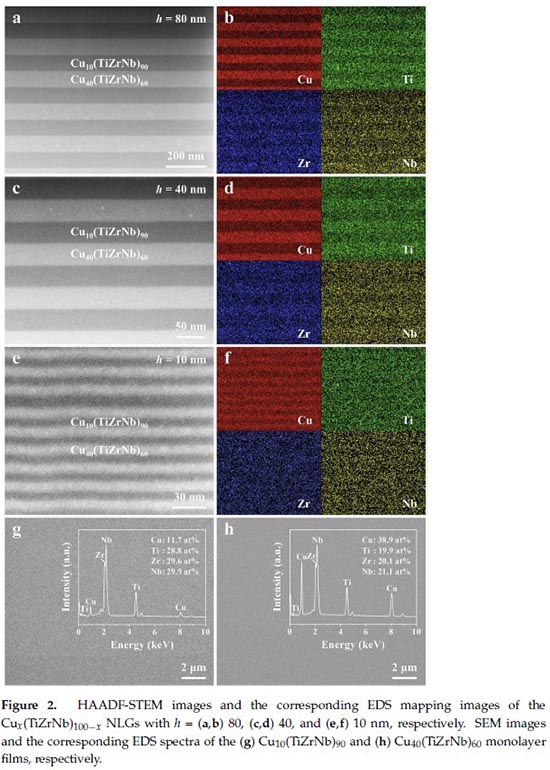
In additions, Prof. Jianjun Li had systematically studied the degrees of shear instability of magnetron sputtering prepared Cux(TiZrNb)100-x NLGs with different layer thicknesses. It was found that the hardness of the designed structure was almost size-independent. Yet, a clear transition in the deformation modes from the cutting-like shear bands to the kinking-like ones was discovered as layer thickness decreased to 10 nm. The resistance to shear instability increases monotonically with the decrease of layer thickness. The improvement in shear instability resistance also comes from the increase in the number of A/A interfaces and the A/A interfaces becoming wavier, which can effectively block the propagation of SBs. Thus, their study provides an easy and flexible route to develop ultra-strong yet highly deformable amorphous alloys that could be widely employed in practical engineering applications.
The research work is published in "Quantifying the Size-Dependent Shear Banding Behavior in High-Entropy Alloy-Based Nanolayered Glass" .
========================================================
========================================================
In additions, Prof. Jianjun Li had systematically studied the degrees of shear instability of magnetron sputtering prepared Cux(TiZrNb)100-x NLGs with different layer thicknesses. It was found that the hardness of the designed structure was almost size-independent. Yet, a clear transition in the deformation modes from the cutting-like shear bands to the kinking-like ones was discovered as layer thickness decreased to 10 nm. The resistance to shear instability increases monotonically with the decrease of layer thickness. The improvement in shear instability resistance also comes from the increase in the number of A/A interfaces and the A/A interfaces becoming wavier, which can effectively block the propagation of SBs. Thus, their study provides an easy and flexible route to develop ultra-strong yet highly deformable amorphous alloys that could be widely employed in practical engineering applications.
The research work is published in "Quantifying the Size-Dependent Shear Banding Behavior in High-Entropy Alloy-Based Nanolayered Glass" .
========================================================
 ========================================================
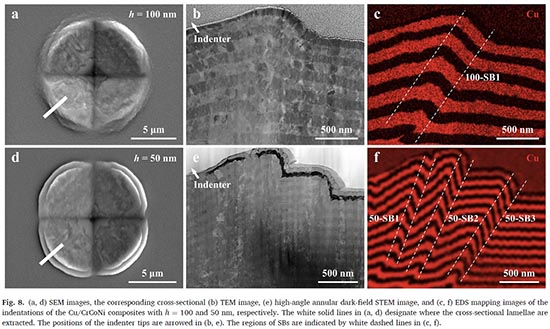
Furthermore, Prof. Jianjun Li had investigated the strengthening and shear instability of Medium/high entropy alloys (M/HEAs)-based nanolayered metallic composites by both nano/microindentation. It had shown that the hardness of the Cu/CrCoNi composites increases monotonically with the decrease of thickness (h), manifesting the trend of "smaller is stronger". Moreover, the degree of shear instability increases with the decrease of the layer thickness. In their theoretical studies, the size-dependent strengthening and plasticity can be respectively captured by the confined layer slip model and the proposed theoretical model. Different from the popular belief, it is found that the shear deformation is mediated by the vertically aligned gain boundaries GBs rather than the horizontal layered interfaces due to the occurrence of the columnar crystal when h <=25 nm. These findings give valuable insights into explaining the behavior of shear deformation for the nanolayered composites that contain M/HEAs as the constituent phases.
The research work is published in "Medium entropy alloy-induced strong size dependence in the strengthening and shear instability of nanolayered metallic composites" .
========================================================
========================================================
Furthermore, Prof. Jianjun Li had investigated the strengthening and shear instability of Medium/high entropy alloys (M/HEAs)-based nanolayered metallic composites by both nano/microindentation. It had shown that the hardness of the Cu/CrCoNi composites increases monotonically with the decrease of thickness (h), manifesting the trend of "smaller is stronger". Moreover, the degree of shear instability increases with the decrease of the layer thickness. In their theoretical studies, the size-dependent strengthening and plasticity can be respectively captured by the confined layer slip model and the proposed theoretical model. Different from the popular belief, it is found that the shear deformation is mediated by the vertically aligned gain boundaries GBs rather than the horizontal layered interfaces due to the occurrence of the columnar crystal when h <=25 nm. These findings give valuable insights into explaining the behavior of shear deformation for the nanolayered composites that contain M/HEAs as the constituent phases.
The research work is published in "Medium entropy alloy-induced strong size dependence in the strengthening and shear instability of nanolayered metallic composites" .
========================================================
 ========================================================
Those high entropy alloy HEA, metallic glass and medium entropy alloys are prepared and fabricated by PTL6S PVD Sputtering System .
========================================================
Those high entropy alloy HEA, metallic glass and medium entropy alloys are prepared and fabricated by PTL6S PVD Sputtering System .
|
| |
|
|
 |
 |
|

