| |
Broad Beam Ion Implanter
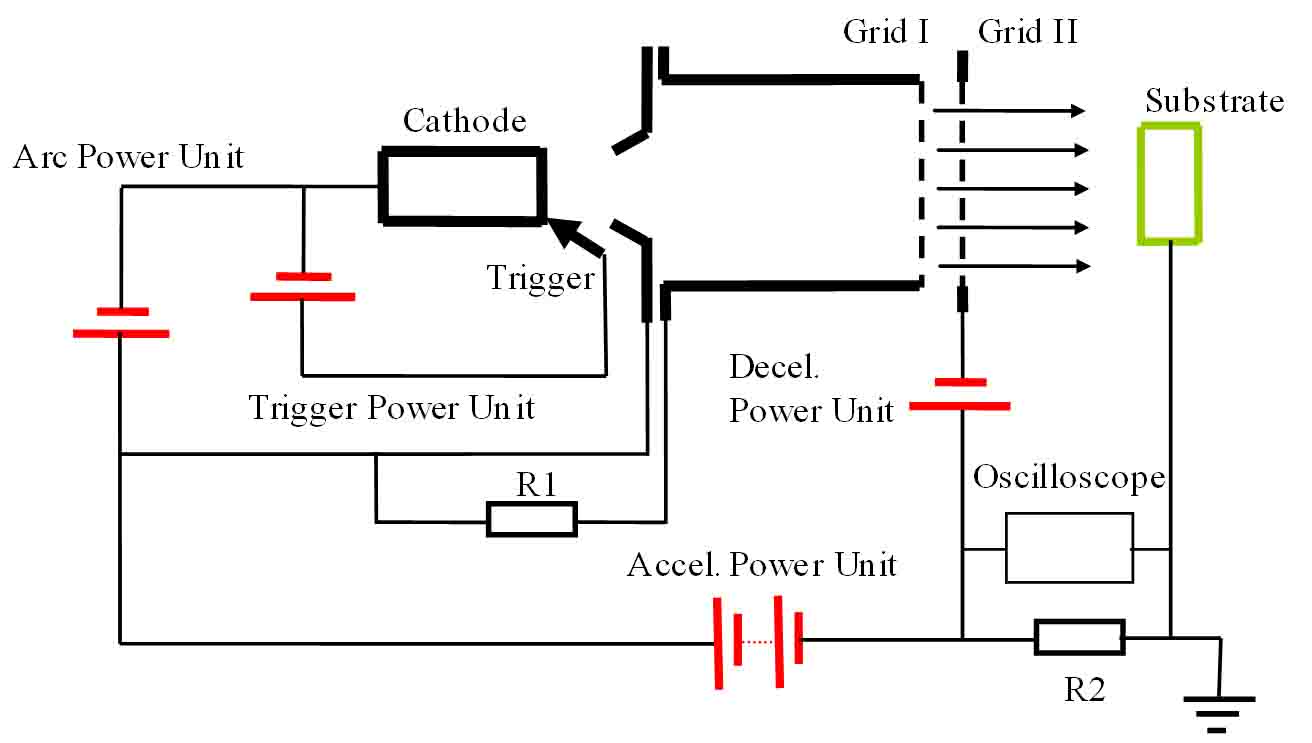
The system has equipped with a pulse-mode metal cathodic vacuum arc source for metallic ion generation. The ions can be extracted by acceleration grid upto 20kV-80kV for ion implantation.
The system possessed with broad ion beam F150mm with high ion fluent is used to perform large area implantation >F150mm to acquire high doping concentration within short processing time (10e17 atom/cm2 will be less than 1 hour). In additions, the off-axis rotated substrate with cooling assemble allows excellent uniform implantation and good implantation quality.
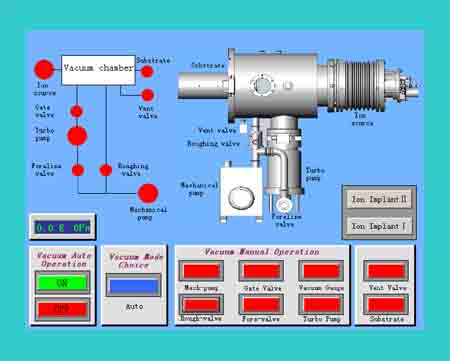
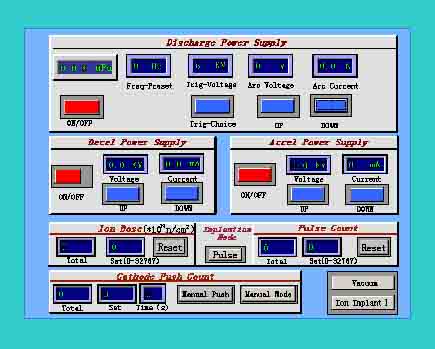
The system is controlled by PLC protocol with Touch Screen Control Panel that offers friendly automatic operation. The implantation dose can be precisely controlled by pulse counter and the process can be highly automated, safe and efficient.

Applications
-
To dope semiconducting, nano/micro-structural materials with foreign elements
-
To produce high energy metal ions for surface modification of ceramic, polymeric and metallic materials
-
To change the surface composition of materials
-
To do the surface irradiation so as to form different microstructures of materials
| Model |
: |
HEMII-50 and HEMII-80 |
| Chamber |
: |
SS 304 steel; F400mm x 500mm |
| Pumping System |
: |
Turbomolecular pump; Mechanical rotary pump; Pneumatic gate valve; Foreline valve; Rounghing valve; Venting valve |
| Ultimate Pressure |
: |
Better than 8 x 10e-5 Pa |
| Substrate |
: |
150mm; Water cooled and satellite rotation |
| Metal Source |
: |
Pulse mode operation; Pulse width 1mS; Pulse frequency 1-30Hz |
| Output Voltage |
: |
20kV-80kV |
| Beam Size |
: |
>F150mm |
| Non-uniformity |
: |
<+/-5% of F150mm |
| Control Panel |
: |
Touch screen PLC control |
| Interlock & Protection |
: |
Vacuum & cooling water interlock; over-current & over voltage protection |
|
|
|
Features
-
Ultra Broad Ion Beam for Large and High Uniform Implantation
-
Widely Adjustable Ion Implantation Voltage
-
Pure Metal and Alloyed Elements Implantation
-
Real-time Implantation Dose Counting or Pulse Number Counting
-
Substrate Independent
-
Easy Touch-control
Product Brochure
Download "HEMII-80 Brochure"
Implanter Characteristic
Download "Ion charge state and velocity datasheet"
Download "SRIM Software" This is a very good free software to calculate the ion projected range and ion distribution in the materials.
For additional product information and pricing contact our specialists at sales@plasmatechnol.com.
Related Scientific Publications
1. K. Feng, X. Cai, Z. G. Li, and P. K. Chu, "Improved Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steel 316L by Ti Ion Implantation", Materials Letters, vol. 68, no. 1, pp. 450 - 452 (2012).
2. K. Feng, T. Hu, X. Cai, Z. G. Li, and P. K. Chu, "Ex Situ and In Situ Evaluation of Carbon Ion-Implanted Stainless Steel Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells", Journal of Power Sources, vol. 199, pp. 207 - 213 (2012).
3. Y. Zhao, G. S. Wu, H. B. Pan, K. W. K. Yeung, and P. K. Chu, "Formation and Electrochemical Behavior of Al and O Plasma-Implanted Biodegradable Mg-Y-RE Alloy", Materials Chemistry and Physics, vol. 132, no. 1, pp. 187 - 191 (2012).
4. K. Feng, G. S. Wu, T. Hu, Z. G. Li, X. Cai, and P. K. Chu, "Dual Ti and C Ion-Implanted Stainless Steel Bipolar Plates in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells", Surface and Coatings Technology, vol. 206, no. 11 - 12, pp. 2914-2921 (2012).
5. R. Z. Xu, G. S. Wu, X. B. Yang, X. M. Zhang, Z. W. Wu, G. Y. Sun, G. Y. Li, and P. K. Chu, "Corrosion Behavior of Chromium and Oxygen Plasma-Modified Magnesium in Sulfate Solution and Simulated Body Fluid", Applied Surface Science, vol. 258, no. 20, pp. 8273 - 8278 (2012).
6. R. Z. Xu, X. B. Yang, K. W. Suen, G. S. Wu, P. H. Li, and P. K. Chu, "Improved Corrosion Resistance on Biodegradable Magnesium by Zinc and Aluminum Ion Implantation", Applied Surface Science, vol. 263, pp. 608 - 612 (2012).
7. Y. Zhao, G. S. Wu, J. Wu, Q. Y. Lu, J. Wu, R. Z. Xu, K. W. K. Yeung, and P. K. Chu, "Improved Surface Corrosion Resistance of WE43 Magnesium Alloy by Dual Titanium and Oxygen Ion Implantation", Thin Solid Films, vol. 529, pp. 407-411 (2013).
8. Y. Zhao, J. Mohammed Ibrahim, W. K. Li, G. S. Wu, Y. F. Zheng, K. W. K. Yeung, and P. K. Chu, "Enhanced Antimicrobial Properties, Biocompatibility, and Corrosion Resistance of Plasma-Modified Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys", Acta Biomaterialia, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 544 - 556 (2014).
9. R. Z. Xu, X. B. Yang, P. H. Li, K. W. Suen, G. S. Wu, and P. K. Chu, "Eelectrochemical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Carbon-Ion-Implanted Magnesium", Corrosion Science, vol. 82, pp. 173 - 179 (2014).
10. W. H. Jin, G. S. Wu, H. Q. Feng, W. H. Wang, X. M. Zhang, and P. K. Chu, "Improvement of Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility of Rare-Earth WE43 Magnesium Alloy by Neodymium Self-Ion Implantation", Corrosion Science, vol. 94, pp. 142 - 155 (2015).
11. W. H. Jin, G. S. Wu, A. Gao, H. Q. Feng, X. Peng, and P. K. Chu, "Hafnium-Implanted WE43 Magnesium Alloy for Enhanced Corrosion Protection and Biocompatibility", Surface and Coatings Technology, vol. 306, Part A, pp. 11 -15 (2016).
|

